Download the list of diagnostic panels and determinations:
Or estimate the approximate cost of an analysis with our diagnostic calculator
greater accuracy
designed by species, clinical process, and age
more information
we analyze all pathogens involved via qPCR
lower cost
all analyses are performed on the same sample
results within hours
complete automated process
The main objective of the diagnosis of infectious diseases is to identify the causative agent(s) in order to apply the most effective treatment and establish the most appropriate preventive measures. It is important to recall that every technique provides a different type of information and that they can complement each other, increasing diagnostic sensitivity and allowing for the precise identification of the etiological agent.
isolation by culture and bacteria identification using MALDI-TOF
1- we select the appropriate samples and grow them on specific culture media
2- we obtain bacteria colonies that are easy and difficult to isolate
3- we place the isolated colonies on the MALDI-TOF plate
4- we use mass spectrometry to obtain the bacterial molecular fingerprint, which is compared with more than 10000 spectra present in its database
5- and we achieve the accurate identification of bacteria at genus and species level
identification: high sensitivity technique
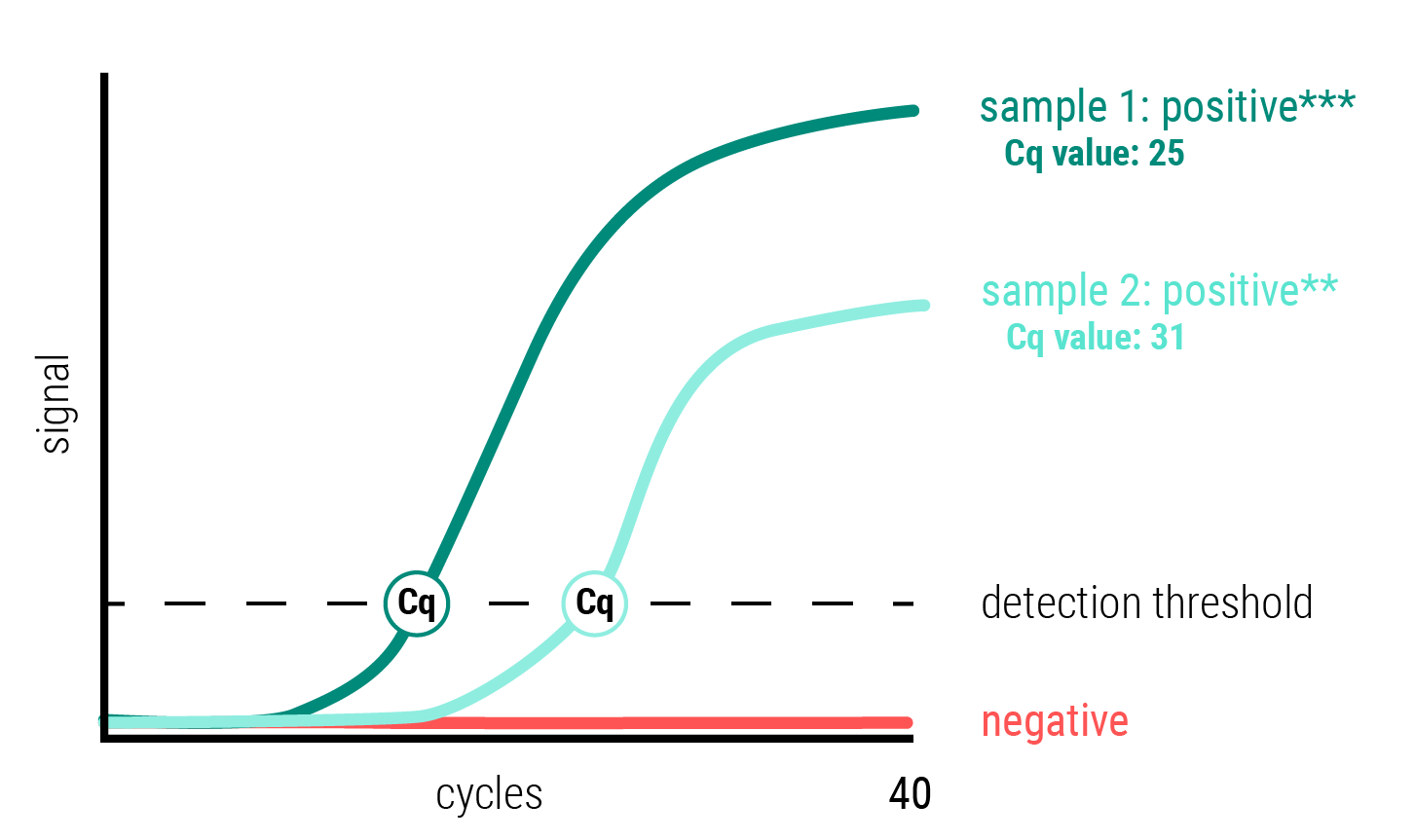
quantification: pdetection of the pathogen concentration present in samples due to Cq value (cycle in which the number of copies exceeds the detection threshold): the lower the Cq value, the higher the concentration of pathogens in the sample
characterization & typification: identifying the toxins, virulence factors, serotypes, etc. of a pathogen allows for the design of autovaccines and other control methods to be applied
differentiation of strains:: differentiation between field strains and vaccine strains
determination of the nucleotide sequence of a gene or genomic region for performing epidemiological studies, determining genotypes, identifying variants or typifying bacterial strains.
evaluation of immune responses: detection of antibodies against infectious agents by immunological techniques (ELISA, agglutination, immunofluorescence, etc.).