Antibiotic sensitivity testing is the measurement of the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics in vitro with the purpose of correlating these results with the clinical efficacy. Different techniques are available for this purpose:
what is the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)?: The lowest concentration of an antibiotic that prevents the visible growth of bacteria
what are the advantages of MIC?
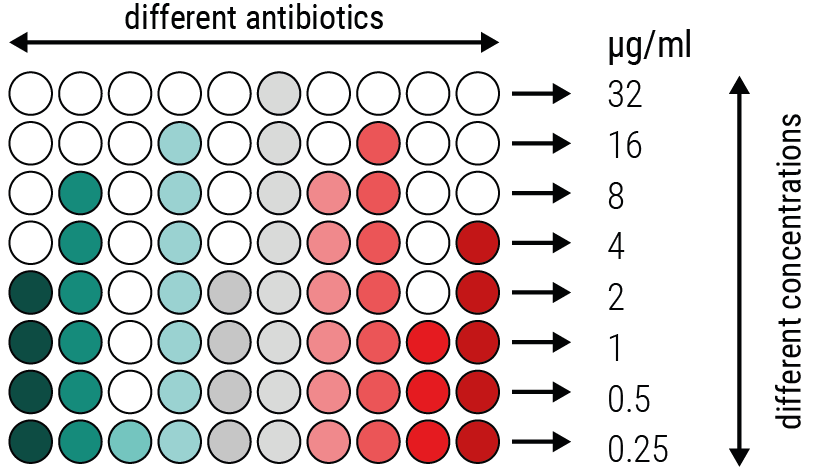
We have developed our own panels to provide you with the best service:
What is an antibiogram used for?: to assess the in vitro susceptibility rates of bacterial strains to a panel of antibiotics
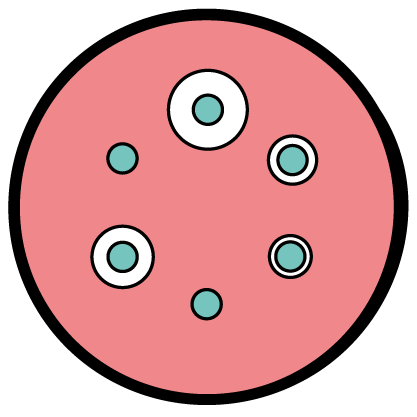
Depending on the antibiotic, the diameter of zone of inhibition of bacterial growth and the clinical cut-off points, bacteria can be classified as sensitive, intermediate or resistant.
 swine
swine
 poultry
poultry
 bovine
bovine
 s. ruminants
s. ruminants
 aquaculture
aquaculture
 rabbits
rabbits
 equine
equine
 pets
pets